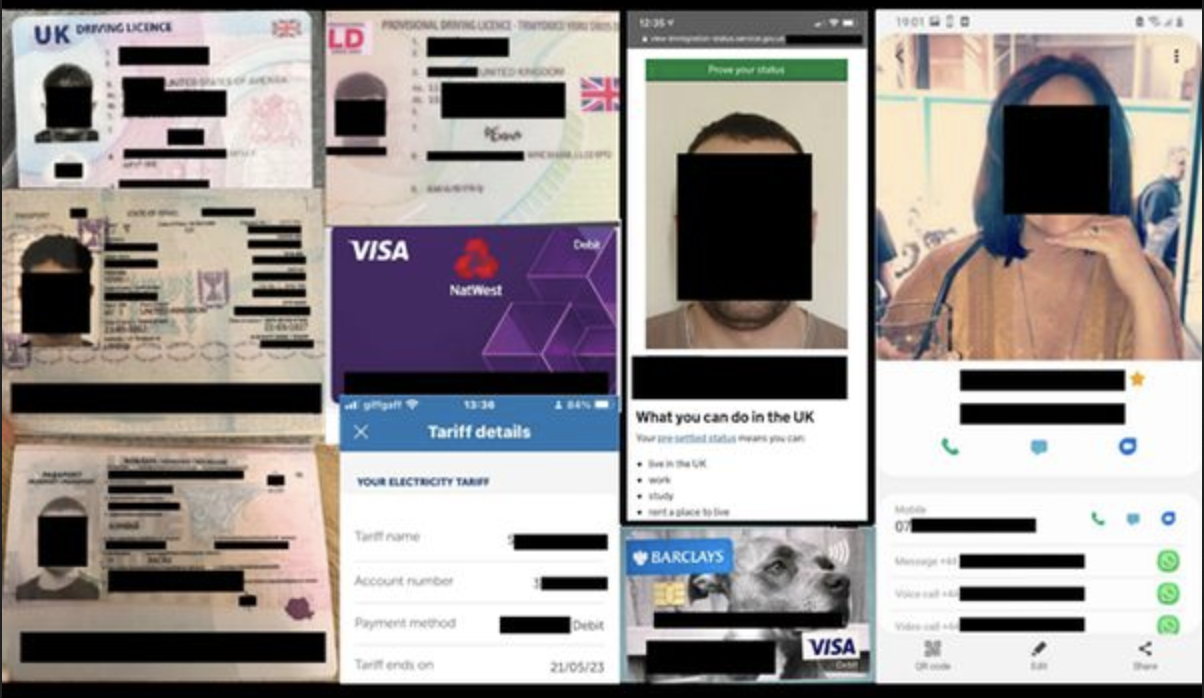
Affiliate Marketing Data Breach Exposed Customer and Vendor Information
In the vast landscape of online commerce, affiliate marketing networks play a pivotal role, connecting sellers, marketers, and consumers in a symbiotic web of transactions. However, this interconnected ecosystem is not immune to exploitation, and the ramifications of a data breach can be profound. Let’s delve into the vulnerabilities of affiliate marketing networks and envision a scenario where a network succumbs to a data breach, laying bare the sensitive information of its users.
Affiliate marketing networks function as intermediaries that facilitate collaboration between sellers (product or service providers) and marketers (affiliates). Marketers promote the sellers’ offerings, earning a commission for every successful sale or lead generated through their efforts. Consumers, in turn, benefit from targeted advertising and potentially discover products tailored to their interests.
In the realm of digital security, an ethical researcher recently played a crucial role in uncovering a data breach of a prominent Affiliate Marketing Network called BuyGoods.com also known as SoftwareProjects. Committed to upholding ethical standards in the cybersecurity domain, this researcher found a non-password protected database that contained the network’s infrastructure. The findings not only exposed weaknesses in BuyGood’s security measures but also paved the way for timely remediation efforts. By responsibly disclosing the discovered vulnerabilities to the network administrators, this ethical security researcher exemplified the vital role that conscientious individuals play in safeguarding user data and fostering a more secure online environment. The report in WebsitePlanet highlights the following risks:
Centralized Data Repositories:
Affiliate marketing networks often centralize user data for streamlined transactions and analytics. However, this concentration creates a single point of failure, making the network susceptible to breaches if not adequately protected.
Inadequate Encryption Protocols:
Insufficient encryption measures leave user data exposed to potential interception by malicious actors. This is particularly concerning when sensitive information like IDs, credit cards, and order details are involved.
Third-Party Risks:
Networks collaborate with various third-party services for functionalities like payment processing and analytics. Each integration introduces a potential vulnerability, and a compromise in any linked service could have cascading effects on the entire network.
Exposed Information:
User profiles, including names, addresses, and potentially sensitive identifiers, are compromised.
Credit Card Details:
The attackers gain access to stored credit card information, posing a severe financial risk to affected users.
Order Information:
Details of past transactions, including products purchased and order histories, are laid bare.
Potential Exploitation by Cybercriminals:
Monetary Theft:
Stolen credit card details are quickly monetized on the dark web, leading to unauthorized transactions and potential financial losses for affected users.
Identity Theft:
Exposed IDs become fodder for identity thieves, who may use the information for malicious activities, including opening fraudulent accounts or committing other forms of impersonation.
Phishing Attacks:
Armed with order information, cybercriminals could launch targeted phishing attacks, attempting to deceive users with seemingly legitimate communications related to their past purchases.
Social Engineering:
Exploiting the personal details revealed in the breach, cybercriminals may engage in social engineering tactics to manipulate users into divulging additional sensitive information.
Mitigating Risks and Strengthening Defenses:
Advanced Encryption:
Implement robust encryption protocols to safeguard user data against unauthorized access.
Regular Security Audits:
Conduct routine security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
User Education:
Educate users on cybersecurity best practices, emphasizing the importance of vigilance against phishing attempts and the safeguarding of personal information.
Incident Response Plan:
Have a well-defined incident response plan in place to minimize damage in the event of a breach, including swift notification to affected users and regulatory bodies.
The BuyGoods data breach serves as a stark reminder of the importance of robust cybersecurity measures within affiliate marketing networks. By understanding and addressing vulnerabilities, these networks can fortify their defenses and ensure the trust and privacy of their users are upheld in an increasingly digital marketplace.

Our team of writers, armed with a healthy dose of caffeine and an overflowing imagination covers wacky and weird news. From politics to pop culture, from bizarre headlines to analysis, we take a sideways glance at the world’s happenings, delivering news in a way that’s informative, entertaining, and occasionally eyebrow-raising.