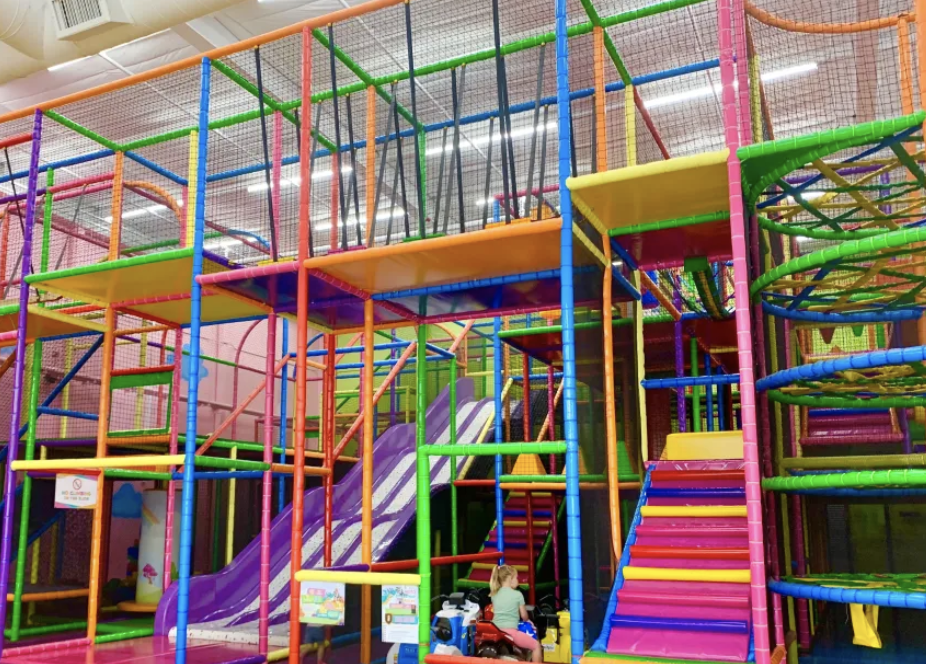
The Hidden Risks: How Offline Businesses Like Indoor Playgrounds Can Face Data Breaches
In an era dominated by digital threats, offline businesses, such as indoor playgrounds and family entertainment centers, may seem immune to data breaches. However, recent incidents have shown that even businesses operating primarily in the physical realm are not immune to the risks of cyberattacks and data breaches. From customer reservations to payment information, the data collected by these businesses can be a goldmine for cybercriminals if not adequately protected.
One significant vulnerability lies in the utilization of digital systems for managing operations and customer data. While these businesses may primarily operate in person, they often rely on digital tools for tasks such as booking reservations, processing payments, and managing customer information. This reliance on digital infrastructure opens up potential avenues for cyberattacks and data breaches.
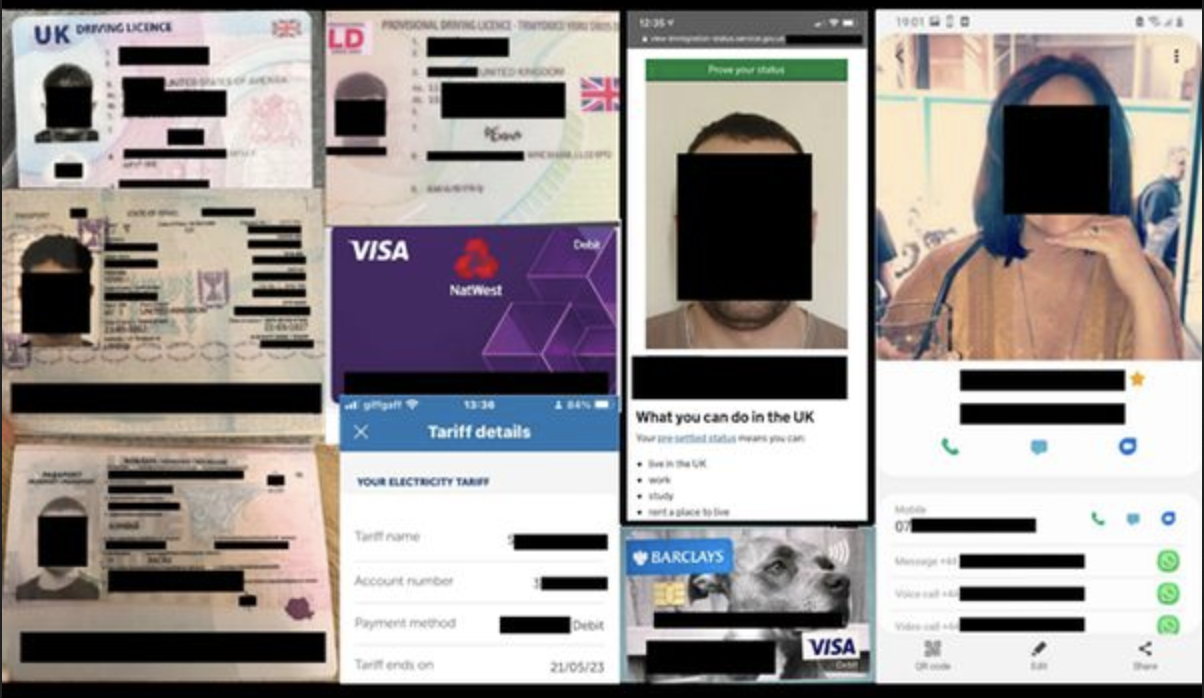
One common way data can be exposed is through the use of non-password protected cloud storage databases. Many businesses, including indoor playgrounds and family entertainment centers, may store sensitive customer information, such as contact details and payment information, in cloud-based databases for ease of access and management. However, if these databases are not adequately secured with strong passwords and encryption measures, they can become easy targets for hackers seeking to steal valuable data.
Additionally, the use of outdated or insecure software systems can leave businesses vulnerable to exploitation by cybercriminals. Hackers often target businesses with outdated software systems that may contain known security vulnerabilities that can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Moreover, human error can also play a significant role in data breaches at offline businesses as in the case of the recent Kids Empire Data Breach. Employees may inadvertently expose sensitive information through actions such as sending unencrypted emails containing customer data or falling victim to phishing attacks that trick them into providing login credentials to malicious actors.
To mitigate the risk of data breaches, offline businesses must prioritize cybersecurity and implement robust security measures. This includes regularly updating software systems to patch known vulnerabilities, securing cloud-based databases with strong passwords and encryption, and providing comprehensive training to employees on cybersecurity best practices.
Furthermore, businesses should conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify and address any potential weaknesses in their systems and processes. By taking proactive steps to protect customer data, offline businesses can safeguard their reputation and maintain the trust of their customers in an increasingly digital world.

Our team of writers, armed with a healthy dose of caffeine and an overflowing imagination covers wacky and weird news. From politics to pop culture, from bizarre headlines to analysis, we take a sideways glance at the world’s happenings, delivering news in a way that’s informative, entertaining, and occasionally eyebrow-raising.